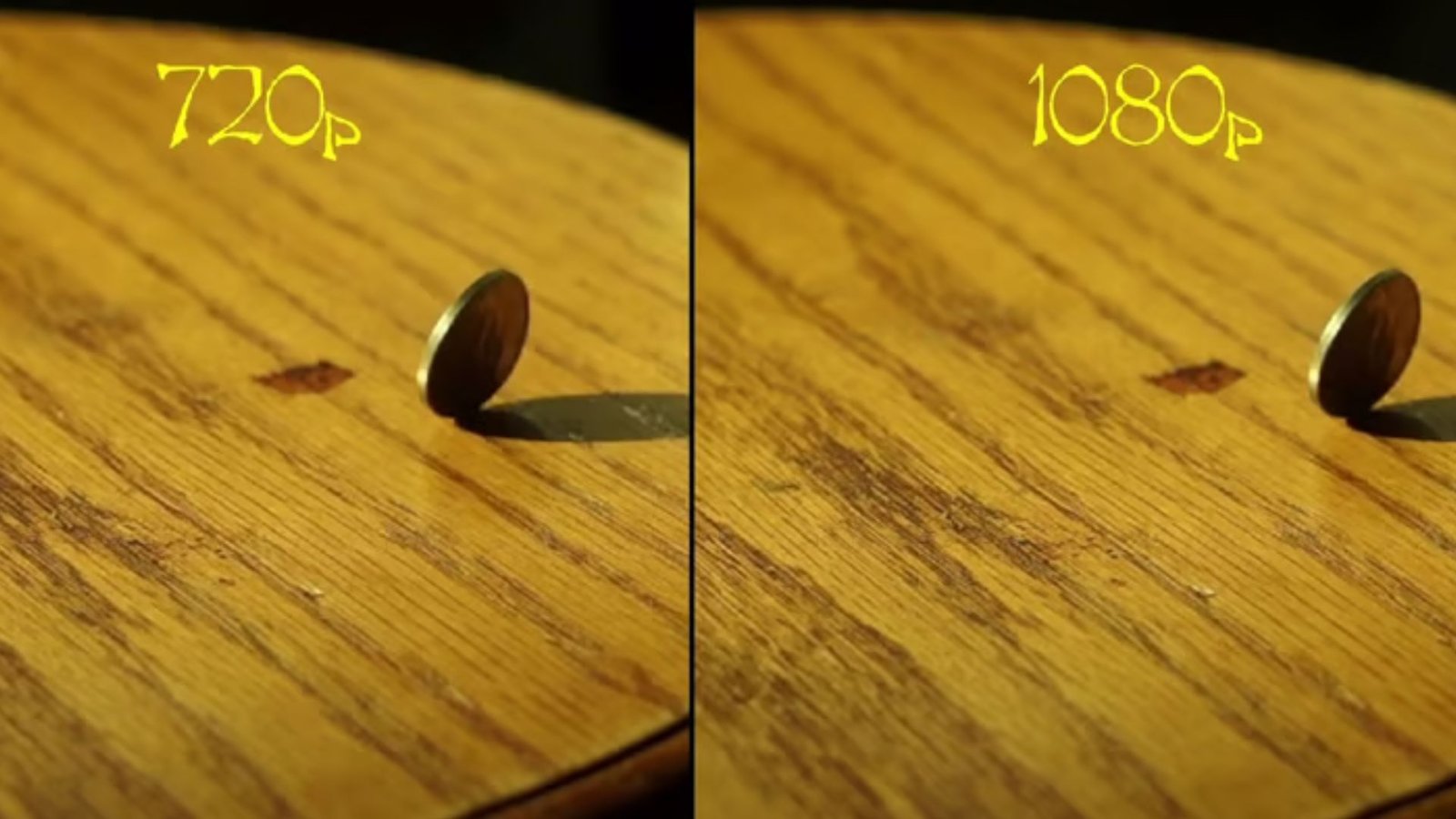
People talk about video quality all the time, but not all terms make sense until you break them down. That is why guides like 720p vs 1080p exist. These terms refer to resolution. They tell you how many pixels make up your picture. More pixels usually means a sharper image, but sharpness is not the only factor that matters.
This article explains the resolution clearly. No jargon. No fluff. You will learn what these numbers mean. You will learn when the difference matters. You will learn how resolution affects real-world use.
What Resolution Actually Means
Resolution refers to pixel count.
Pixels are tiny dots.
Each pixel shows color and brightness.
More pixels mean more detail.
Video resolution is written like this:
- Width x height
- Example: 1280 x 720
- Example: 1920 x 1080
These numbers tell you how many pixels are in the image.
What 720p Means in Practical Terms
720p equals 1280 x 720 pixels.
That is:
- About 921,600 total pixels
Each video frame displays that many tiny dots.
Less detail than higher resolutions, but still clear in many settings.
What 1080p Means in Practical Terms
1080p equals 1920 x 1080 pixels.
That is:
- About 2,073,600 total pixels
More than double the pixel count of 720p.
Each frame has more detail.
The image looks sharper. Especially on bigger screens.
Sharpness Difference You Can See
More pixels mean more clarity.
1080p images show:
- Finer edges
- Clearer text
- Less blurriness
Especially on screens larger than ~32 inches.
On smaller screens, the difference shrinks.
Screen size affects the visibility of detail.
How Distance Changes What You Perceive
Viewing distance changes perception.
Close viewing makes flaws obvious.
Far viewing hides flaws.
A small TV viewed from many feet away may look similar in 720p and 1080p.
Distance matters almost as much as resolution.
Why 1080p Became the Standard
1080p replaced older formats because:
- More pixels improve clarity
- It supports widescreen
- Content became available in higher quality
- Streaming services adopted it
Most modern broadcasts default to 1080p.
1080p feels sharp without needing 4K.
Bandwidth and File Size Differences
More pixels mean more data.
1080p files are larger than 720p files.
Streaming 1080p:
- Consumes more bandwidth
- Requires faster internet
Download feeds must keep up.
720p streams may buffer less on slow connections.
Internet speed affects real-world performance.
Gaming and Frame Rates
In gaming, resolution competes with frame rate.
More pixels take more GPU power.
720p may allow:
- Higher frame rates
- Lower graphics settings
1080p may sacrifice frame rate on older hardware.
Players who value smooth motion may prefer lower resolution.
Frame rate matters for gaming responsiveness.
Cameras and Recording Devices
Devices record at different resolutions.
Many budget cameras do 720p.
More advanced cameras do 1080p.
Higher resolution recordings:
- Show more detail
- Look better when editing
- Crop more flexibly without losing quality
Professional edits benefit from higher resolution source footage.
Smartphone Screens and Pixel Density
Smartphones use pixel density.
Smaller screens pack pixels tightly.
What looks sharp at a normal distance may not change much between 720p and 1080p on a phone.
A 6-inch screen:
- May not show a big difference unless you look closely
- Depends on pixel density (PPI)
Higher PPI improves perceived sharpness.
Streaming Services and Quality Choices
Streaming platforms adjust based on connection.
They offer:
- 480p
- 720p
- 1080p
- 4K
Users with slower internet may default to 720p. That reduces buffering.
Users with fast connections stream 1080p.
Many services show “HD” for 720p and 1080p. But 1080p has a higher pixel count.
When 720p Still Makes Sense
720p works well when:
- Screens are small
- Internet speeds are limited
- File size matters
- Gaming preferences favor frame rate
It holds up on:
- Tablets
- Budget laptops
- Older TVs
It still provides a clear picture for everyday use.
When 1080p Is Worth It
1080p is better when:
- Screen size is large
- You want sharper detail
- You edit the video
- You watch high-quality content
It shows edges clearly. It handles text better. It improves immersion.
The Impact on Battery Life
Higher resolution uses more power.
1080p displays:
- Consume more battery
- Require more GPU effort
720p displays:
- Last longer per charge
- Use less processing power
For mobile devices, this trade-off matters.
Battery life is a real-world factor.
Internet Data Usage
Streaming at 1080p uses more data than 720p.
720p:
- Uses less bandwidth
- Saves data caps
1080p:
- Uses more bandwidth
- Looks better on big screens
People with data limits may choose a lower resolution.
Editing and Storage Considerations
1080p recordings take:
- More storage
- More editing power
720p:
- Requires less storage
- Easier to edit on basic computers
Content creators must balance quality and workflow.
Why Resolution Isn’t Everything
Other factors matter too:
- Color accuracy
- Contrast
- Refresh rate
- Encoding quality
Two videos with the same resolution can still look different.
Resolution is only one piece of quality.
Display Technology Matters
LCD, LED, OLED all display pixels differently.
OLED:
- Shows deeper blacks
- Improves perceived contrast
LCD:
- May look flatter
- Depends on backlight quality
Resolution matters less when display quality is low.
How Compression Affects Quality
Streaming compresses video.
Compression can:
- Reduce detail
- Introduce artifacts
- Blur edges
A compressed 1080p video may look worse than a clean 720p file.
Encoding quality affects real-world clarity.
Why Some People Prefer Lower Resolution
Lower resolution can feel smoother.
Some prefer:
- Faster loading
- Consistent playback
- Less buffering
Not everyone needs the sharpest image.
Use case matters.
Future Trends: 4K and Beyond
4K has more pixels than 1080p.
It expands the detail even further.
But:
- Not every screen uses 4K
- Internet limits still matter
- Content availability varies
1080p remains relevant. Not everyone needs 4K yet.
Real-World Comparison: Side-by-Side
In side-by-side tests:
- 1080p looks clearer
- Fine detail appears sharper
- Text edges look crisper
On small screens:
- Differences shrink
- Distance blurs detail
Context always matters.
Decision Guide: When to Choose Which
Ask:
- What is the screen size?
- What is internet speed?
- What is device power?
- What matters more: detail or performance?
Choose 720p when:
- Speed matters
- File size matters
- Hardware is limited
Choose 1080p when:
- Detail matters
- The screen is large
- Bandwidth is available
Final Thoughts on Resolution Choices
Resolution choices influence experience.
720p still works in many everyday cases.
1080p elevates clarity and detail.
Neither is perfect for every scenario.
Know your needs.
Match resolution to use case.
Balance performance with quality.
With clearer expectations, you can choose the format that fits you.